OSCAD: ein kleines Beispiel-Projekt
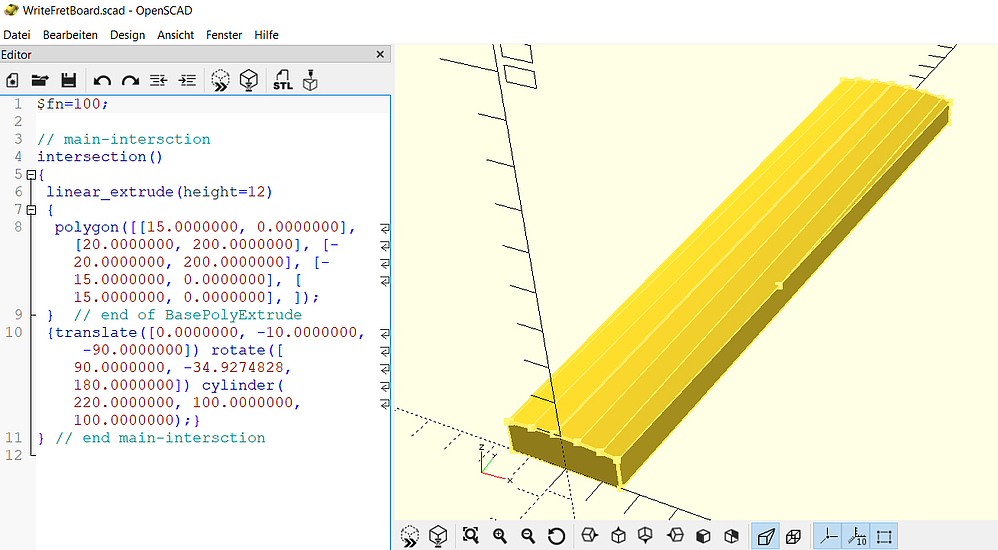
Abb.: Beispiel-Griffbrett, links der erzeugte OSCAD-Quellcode
Hier ist der python-Code, der mit Hilfe von Open Scad ein 3d-Modell eines einfachen Griffbretts erzeugt.
Das Griffbrett hat eine trapezförmige Grundfäche und ist an der oberen Fläche gerundet.
from zutils.ZGeom import Point
from zutils.OSCNode import OSCRoot, OSCExtrudeLin, OSCCombination, OSCCylinder, OSCPolygon
####################################################
def test_fretboard():
'''
Create a simple fretboard with a trapezoidal shape and a rounded upper fret surface
'''
OSCRoot.s_quality = 100 # how fine shall circles be cut into polygones?
# create the main root node:
root = OSCRoot('rootNode')
# create the main boolean intersection:
intersection = OSCCombination('main-intersction', 'intersection')
root.add(intersection)
# the extrusion for the fretboard blank:
extrude = OSCExtrudeLin('BasePolyExtrude', 12)
intersection.add(extrude)
# create a polyline as 4 corners of the fretboard base
wU = 15
wL = 20
l = 200
p1 = Point(wU)
p2 = Point(wL, l)
p3 = Point(-wL, l)
p4 = Point(-wU)
basePoly = OSCPolygon('fretboard-base-poly', [p1, p2, p3, p4, p1])
extrude.add(basePoly)
# create the cylinder for the rounded upper surface:
r = 100
c = Point(0, -10, -r + 10)
cylinder = OSCCylinder('rounding-cylinder', c, Point(0, 1), 220, r)
intersection.add(cylinder)
# save scad file:
root.writeScadTo('/d/python/zutils/code-examples/WriteFretBoard.scad')
# just to visualize the hierarchical node structure (not neccessary for function):
root.printStructure()
############################################
# do it:
test_fretboard()
Der Output des letzten Befehls (root.printStructure()) sieht dann so aus:
root | "rootNode"
-intersection | "main-intersction"
--extrusion | "BasePolyExtrude"
---polygon | "fretboard-base-poly"
--cylinder | "rounding-cylinder"